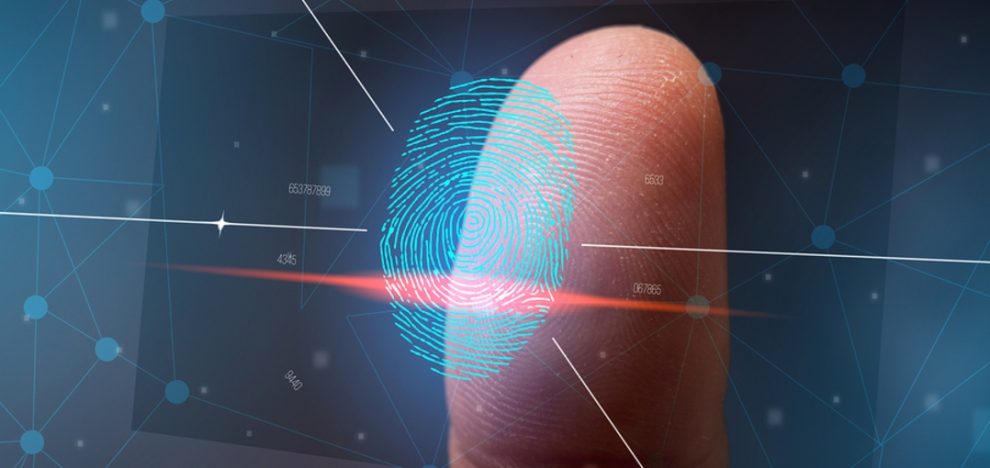
Unlocking a phone with a fingerprint, paying for groceries with a face scan, accessing a building with an iris scan—biometric security has become increasingly commonplace, promising a seamless blend of convenience and security.
But as these technologies permeate our lives, a growing chorus of concerns has emerged, questioning their potential for misuse, privacy violations, and even discrimination.
The Allure of Biometrics
Biometrics offer several key benefits driving their widespread adoption:
- Convenience: Biometrics eliminate the need to remember and manage passwords or carry physical keys.
- Security: Biometric data is unique to each individual, making it more difficult to forge or replicate than traditional security measures.
- Efficiency: Biometric authentication can be faster and more efficient than traditional methods, especially in high-traffic areas.
The Backlash Brews
However, a backlash against biometric security has emerged around three key concerns:
- Privacy Concerns: Biometric data is highly personal and can reveal sensitive information about individuals, such as health conditions or genetic predispositions.
- Data Security Risks: Biometric databases can be hacked, stolen, or misused by governments or corporations for surveillance or profiling.
- Discrimination Potential: Biases in algorithms or data collection could lead to discrimination based on race, gender, or other factors.
Facial Recognition: A Lightning Rod for Controversy

Facial recognition has emerged as one of the most hotly debated biometric technologies:
- Widespread Adoption: Facial recognition is one of the most widely used biometric technologies, deployed in airports, retail stores, and even public spaces.
- Accuracy Concerns: Studies have raised concerns about the accuracy of facial recognition algorithms, particularly for people of color and women.
- Surveillance Fears: The potential for widespread facial recognition surveillance has sparked fears of a “Big Brother” society where individuals are constantly monitored.
Finding the Balance
The challenge lies in harnessing the benefits of biometric security while safeguarding individual rights and privacy. Here are some key considerations:
- Strong Data Protection Laws: Clear regulations are needed to govern the collection, storage, and use of biometric data, ensuring transparency and accountability.
- User Consent and Control: Individuals should have meaningful control over their biometric data, including the ability to opt out or delete it.
- Algorithmic Bias Mitigation: Regular audits and testing are crucial to identify and address biases in biometric algorithms.
- Public Education and Awareness: Raising awareness about the potential benefits and risks of biometric technology is essential to foster informed public debate and decision-making.
The future of biometric security depends on striking a delicate balance between convenience and security, innovation and responsibility. Only by addressing these concerns head-on can we ensure that these technologies enhance our lives without compromising our fundamental rights.














Add Comment