Data is the fuel that drives innovation, powering everything from AI-powered healthcare to personalized education. But when that data lacks diversity and inclusion, it can perpetuate harmful biases and inequalities. This is where synthetic data generation (SDG) emerges as a powerful tool, offering the potential to create more representative datasets for social good.
The Problem with Biased Data
Real-world datasets often reflect existing societal biases, leading to:
- Underrepresentation: Certain groups, like minorities or disabled individuals, may be absent or have limited representation, skewing algorithms and analyses.
- Algorithmic bias: Biased data can train AI systems to perpetuate those biases, leading to discriminatory outcomes in areas like loan approvals or facial recognition.
- Privacy concerns: Collecting real-world data raises privacy concerns, especially for sensitive information.
Enter Synthetic Data: A Promising Solution
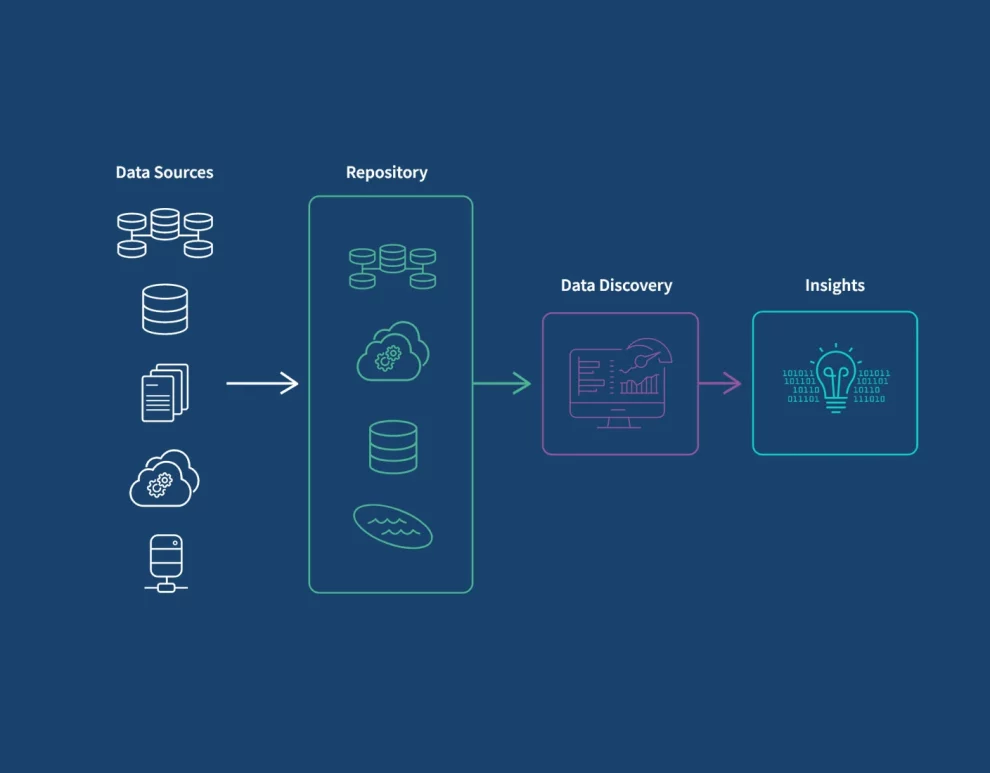
SDG creates realistic, artificial data that mimics the statistical properties of real data. This allows researchers and developers to:
- Augment existing datasets: Increase the representation of underrepresented groups while preserving privacy.
- Control and manipulate data: Create diverse scenarios for testing and analysis without real-world limitations.
- Reduce privacy risks: Protect sensitive personal information by using synthetically generated data instead.
Building Diverse and Inclusive Datasets with SDG
Several techniques are used for SDG, each with its strengths and limitations:
- Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs): Two neural networks compete, creating increasingly realistic synthetic data.
- Variational Autoencoders (VAEs): Learn the underlying data distribution and generate new data points within that distribution.
- Statistical methods: Use statistical models to generate data based on known parameters and distributions.
The key to achieving diversity and inclusion in SDG lies in:
- Understanding real-world biases: Analyzing existing datasets to identify and avoid perpetuating biases in synthetic data.
- Incorporating diverse inputs: Using data from various sources and demographics to ensure broad representation.
- Human oversight and evaluation: Regularly evaluating the generated data for bias and ensuring alignment with ethical guidelines.
Applications for Social Good
SDG has the potential to revolutionize numerous areas for social good:
- Healthcare: Train AI models to diagnose diseases in underrepresented populations or develop personalized treatments without real-patient data.
- Finance: Create inclusive credit scoring models that don’t perpetuate historical biases against certain groups.
- Education: Develop personalized learning systems that cater to diverse learning styles and backgrounds.
- Criminal justice: Analyze data for potential biases in algorithms used for risk assessment or recidivism prediction.
Challenges and Considerations
While promising, SDG is not without challenges:
- Technical complexity: Implementing and using SDG effectively requires technical expertise and computational resources.
- Data quality: The quality of synthetic data depends heavily on the quality of the training data and underlying algorithms.
- Potential for misuse: Like any technology, SDG could be misused to create synthetic data that reinforces harmful stereotypes.
Conclusion: A Bridge to a More Equitable Future
Synthetic data generation presents a powerful tool for creating more diverse and inclusive datasets, paving the way for fairer and more equitable outcomes across various domains. By addressing the challenges and prioritizing ethical considerations, we can harness the potential of SDG to build a more just and inclusive future for all.













Add Comment