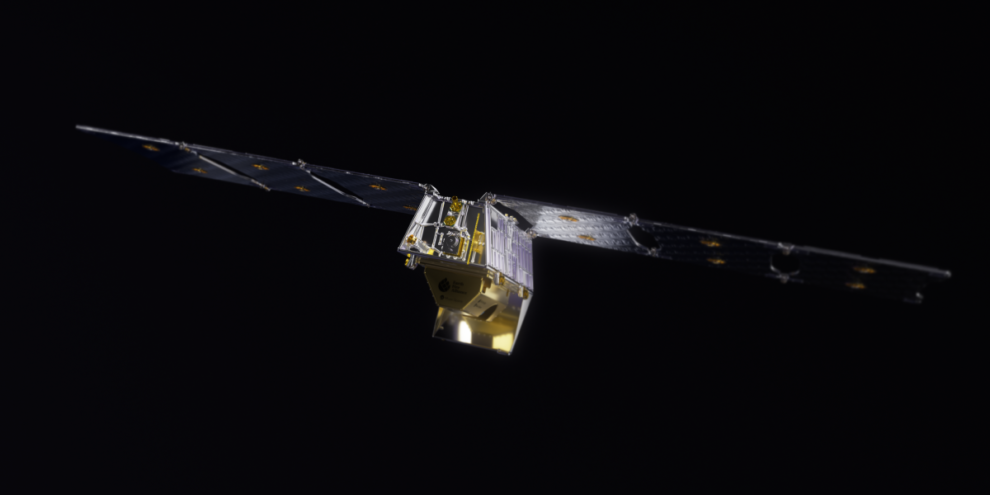
Over the weekend, a groundbreaking milestone was achieved in the fight against wildfires. The first satellite of the Google-backed FireSat constellation successfully reached orbit, marking the beginning of a transformative era in wildfire detection and monitoring. This ambitious project, spearheaded by Muon Space and supported by a coalition of organizations, aims to revolutionize how wildfires are tracked and managed, offering unprecedented accuracy and speed.
The FireSat constellation is poised to deliver revolutionary capabilities, with more than 50 satellites planned to form a comprehensive network capable of imaging nearly all of Earth’s surface every 20 minutes. While the initial phase will involve just three satellites, the full constellation will eventually revisit every point on the globe twice daily when operational in 2026. This ambitious timeline reflects the urgent need for advanced tools to combat the growing threat of wildfires, which have intensified in recent years due to climate change and human activity.
A Game-Changing Satellite Launch
The first satellite in the FireSat constellation was built by Muon Space and launched aboard SpaceX’s Transporter 13 mission on March 14 from Vandenberg Space Force Base. This launch marks a pivotal moment in the development of satellite-based wildfire monitoring, showcasing the potential of private-public partnerships in addressing environmental challenges. The satellite’s sensor suite comprises six-band multispectral infrared cameras, specifically designed to detect wildfires from a distance. These advanced sensors allow the satellite to capture high-resolution images, providing critical data to firefighting teams in real time.
Traditional wildfire tracking methods rely heavily on aerial photography via airplanes or repurposed low-resolution satellite imagery. While these approaches have been useful, they come with significant limitations. Aerial photography is expensive and restricts how frequently updates can be obtained, while repurposed satellite imagery suffers from low resolution and lacks specialized sensors tailored to wildfire detection. The FireSat constellation addresses these shortcomings by producing five-meter resolution imagery, offering firefighters precise and timely updates on a fire’s location and behavior.
Bridging the Gap Between Technology and Ecology
The FireSat constellation represents a collaborative effort between Muon Space and the Earth Fire Alliance, a nonprofit organization supported by Google, Muon Space, the Environmental Defense Fund, the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation, and the Minderoo Foundation. This diverse coalition brings together expertise in technology, environmental science, and philanthropy, ensuring that the project aligns with both scientific rigor and humanitarian goals.
Google’s involvement in the FireSat initiative underscores its commitment to leveraging technology for social good. As wildfires continue to devastate ecosystems and communities worldwide, innovative solutions like FireSat are essential for mitigating their impact. By providing near real-time updates, the constellation enables rapid response and strategic planning, saving lives and minimizing property damage.
The Future of Wildfire Management
As the FireSat constellation expands, it will offer unparalleled capabilities in wildfire detection and monitoring. With its ability to revisit every point on Earth twice daily, the constellation will provide continuous coverage, ensuring that no fire goes unnoticed. The high-resolution imagery produced by the satellites will enable firefighters to track fires with unprecedented accuracy, allowing them to allocate resources more effectively and prevent the spread of flames.
The initial phase of the project, involving just three satellites, lays the groundwork for the eventual deployment of a full constellation. This phased approach ensures that the technology is thoroughly tested and refined before scaling up. By 2026, when the full constellation is operational, firefighters will have access to a wealth of data that can inform their decisions and improve outcomes.
A Vision for a Safer World
The FireSat constellation is more than just a technological advancement; it represents a vision for a safer and more sustainable world. By harnessing the power of satellite technology, the project aims to empower communities to better prepare for and respond to wildfires. The collaboration between Muon Space and the Earth Fire Alliance highlights the potential of cross-sector partnerships in driving meaningful change.
As wildfires continue to pose a significant threat to global ecosystems and human safety, initiatives like FireSat offer hope for a future where we can mitigate their impact. By investing in cutting-edge technology and fostering partnerships, we can build a more resilient world capable of adapting to the challenges of a changing climate.
In conclusion, the successful launch of the first FireSat satellite marks a historic moment in the fight against wildfires. With its advanced sensors and global coverage, the FireSat constellation promises to transform wildfire detection and management, providing firefighters with the tools they need to protect lives and preserve ecosystems. As the project progresses, it will undoubtedly serve as a model for future initiatives aimed at addressing environmental challenges through innovation and collaboration.














Add Comment