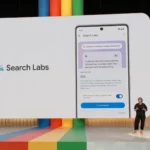
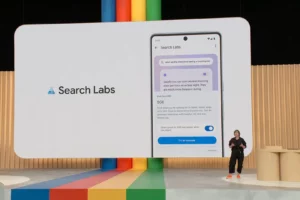
Google and Samsung have collaborated to enhance Bluetooth Auracast support for hearing aids, bringing improved functionality to millions of users worldwide. During the release of Android 16 Beta 3, Google announced that Samsung smartphones and tablets running One UI 7.0 (based on Android 15) would gain enhanced support for hearing aids from select brands through Bluetooth LE Audio and Auracast. This feature is set to expand to Android devices from other manufacturers with the Android 16 update.
This development marks a major milestone in the evolution of Bluetooth LE Audio, which was introduced to address the limitations of traditional Bluetooth technology. By leveraging the power of Bluetooth LE, Auracast offers a more efficient and reliable way to transmit audio signals, paving the way for smarter and more inclusive experiences.
One UI 7.0: Better Support for Hearing Aids
Samsung’s One UI 7.0 update introduces groundbreaking improvements in hearing aid compatibility, thanks to its integration with Bluetooth LE Audio and Auracast. This feature allows Galaxy devices to connect seamlessly with hearing aids from brands like GN Hearing and Starkey, offering users a richer and more intuitive listening experience.
The compatibility extends beyond simple pairing. With One UI 7.0, Samsung Galaxy devices enable users to stream Auracast broadcasts in public spaces such as airports, museums, tourist spots, and theaters. Imagine walking into an airport concourse and instantly receiving real-time announcements directly into your hearing aids, or tuning into guided tours at historical landmarks without the need for cumbersome equipment. This level of accessibility transforms daily life for individuals with hearing impairments, making public spaces more inclusive and navigable.
The Evolution of Auracast on Samsung Devices
Samsung’s journey with Auracast began with the introduction of Bluetooth LE Audio support on its Galaxy Buds 2 Pro and newer Galaxy Buds models. With the One UI 5.1.1 update, Samsung enabled users to join Auracast streams, allowing them to tune into broadcasts from nearby devices. The One UI 6.1 update took this a step further by introducing the ability to create Auracast streams using Galaxy devices, opening up new possibilities for collaboration and shared audio experiences.
Now, with One UI 7.0, Samsung has refined Auracast to support hearing aids, marking a significant advancement in assistive technology. This integration ensures that users can enjoy consistent, high-quality audio streaming directly to their hearing aids, eliminating the need for additional adapters or bulky devices.
What Is Bluetooth Auracast?
At the heart of this breakthrough lies Bluetooth LE Audio, a revolutionary protocol designed to replace traditional Bluetooth technology. Auracast, a key feature of LE Audio, allows devices to broadcast audio signals to multiple receivers simultaneously, creating a more efficient and scalable audio-sharing ecosystem.
Bluetooth LE Audio introduces several advantages over its predecessor. It consumes less power, supports higher-quality audio, and enables simultaneous connections to multiple devices. These enhancements make Auracast an ideal solution for environments where multiple users need to access the same audio feed, such as concerts, conferences, or public transportation hubs.

Simplified Access Through QR Codes
One of the standout features of Auracast is its ease of use. Google and Samsung have partnered with Bluetooth SIG to introduce standardized QR codes for joining Auracast audio broadcasts. Instead of navigating complex settings menus, users can simply scan a QR code with their smartphone camera to connect to an audio stream. This intuitive approach eliminates the guesswork and frustration associated with traditional pairing methods, making Auracast accessible to everyone.
QR codes are particularly useful in public spaces, where signage can guide users to specific audio feeds. For instance, a museum might place QR codes near exhibits, allowing visitors to listen to detailed descriptions or commentary directly through their hearing aids. Similarly, airports and train stations could deploy QR codes to provide real-time announcements, ensuring that all passengers receive critical information regardless of their hearing abilities.
Expanding Reach Across Android Devices
While Samsung’s Galaxy devices lead the charge with One UI 7.0, Google has announced that the same Auracast feature will be available on Pixel devices with the Android 16 update. This rollout signifies Google’s commitment to improving accessibility across its ecosystem, ensuring that users of all Android devices can benefit from this innovative technology.
Additionally, Google has indicated that other Android manufacturers will likely adopt Auracast support for hearing aids with the Android 16 update. This widespread adoption could herald a new era of inclusivity in the tech industry, where accessibility features become standard across all devices.
The Broader Impact of Bluetooth LE Audio
Bluetooth LE Audio’s impact extends far beyond hearing aids. Its efficiency and scalability make it ideal for a wide range of applications, from fitness trackers to smart home devices. For instance, fitness enthusiasts can stream workout instructions directly to their headphones, while homeowners can control smart appliances with voice commands delivered through their hearing aids.
Moreover, Bluetooth LE Audio paves the way for new use cases that were previously impossible with traditional Bluetooth. Imagine a concert venue broadcasting live performances to attendees’ personal devices, or a theater providing synchronized subtitles for hearing-impaired patrons. These scenarios demonstrate the transformative potential of Auracast and Bluetooth LE Audio.
A Step Toward a More Inclusive Future
The integration of Bluetooth Auracast with hearing aids represents a monumental step forward in creating a more inclusive digital world. By enabling seamless audio streaming to hearing aids, Google and Samsung have empowered individuals with hearing impairments to participate fully in society. Public spaces, educational institutions, and entertainment venues can now offer equal access to information and experiences, fostering a sense of belonging and empowerment.
This initiative also underscores the importance of collaboration in technological innovation. By working together with Bluetooth SIG and other stakeholders, Google and Samsung have demonstrated the power of partnerships in driving meaningful change. As more devices adopt Bluetooth LE Audio and Auracast, we can expect to see a ripple effect of positive outcomes across industries and communities.
Google and Samsung’s efforts to enhance Auracast support for hearing aids mark a turning point in the evolution of Bluetooth technology. By introducing Bluetooth LE Audio and Auracast, these companies have opened the door to a more connected and inclusive future. Whether you’re streaming announcements at an airport, enjoying a concert, or exploring a museum, Auracast ensures that no one is left behind.
As the Android 16 update rolls out and other manufacturers embrace this technology, we can anticipate a world where accessibility is no longer an afterthought but a core tenet of innovation. For individuals with hearing impairments, this means greater independence, freedom, and participation in the digital age. And for society as a whole, it signals a commitment to building a world where everyone, regardless of ability, can thrive.













Add Comment