Finding your laptop refusing to turn on can be incredibly frustrating. One minute you’re happily working or browsing away, the next minute your screen is blank and pressing the power button does nothing. Don’t panic just yet though! With some targeted troubleshooting, you can get to the bottom of the issue and have your device up and running again in no time.
Before you decide that the laptop is a lost cause and shell out for an expensive repair or replacement, try working through the following steps. We’ll cover all the basics, from checking connections to resetting the BIOS. With persistence and patience, you should be able to determine what’s preventing your laptop from turning on and take appropriate action to fix it.
Step 1: Check the Basics
First things first, we need to rule out any obvious issues that don’t require dismantling the laptop or tinkering with software settings. Let’s confirm all the basic prerequisites for powering on the device are satisfied:
Is it plugged in?
Make sure the AC power adapter is securely plugged into both the wall outlet and the laptop itself. Faulty connections are one of the most common reasons a laptop won’t start up. Examine the DC plug carefully for any damage or bent pins as well. If available, try connecting to a different wall outlet to ensure there isn’t an issue with that particular power source.
Is the AC adapter working correctly?
Inspect the power cord and power brick for any visible signs of damage, fraying, or exposed wires. If you have access to another compatible AC adapter, switch them out to see if that’s the culprit. Adapters can wear out over time or be damaged by pinched/bent cords.
Is the battery removable? If so, try without it.
For laptops with removable batteries, take out the battery entirely and attempt to turn the laptop on solely using wall power. If it powers up normally, the battery itself might be defective and preventing the laptop from receiving consistent power. Test with another compatible laptop battery or simply replace the current one.
Step 2: Reset the Power System
If you’ve confirmed the basics are all working, the next step is to power cycle the laptop. This clears any stuck processes or faulty electrical connections preventing startup.
Force shut down a frozen machine
If the laptop is unresponsive and seems frozen, hold down the power button continuously for 10-15 seconds to force a system shutdown. This will disengage any components stuck in an in-between power state.
Disconnect all peripherals
Unplug any devices connected to the laptop, such as external hard drives, USB drives, headphones, etc. You want to isolate the machine and eliminate any interference from accessories.
Remove battery and disconnect AC adapter
This discharges any residual static electricity that could be preventing normal power up. Removing the battery has the added effect of resetting the laptop’s CMOS.
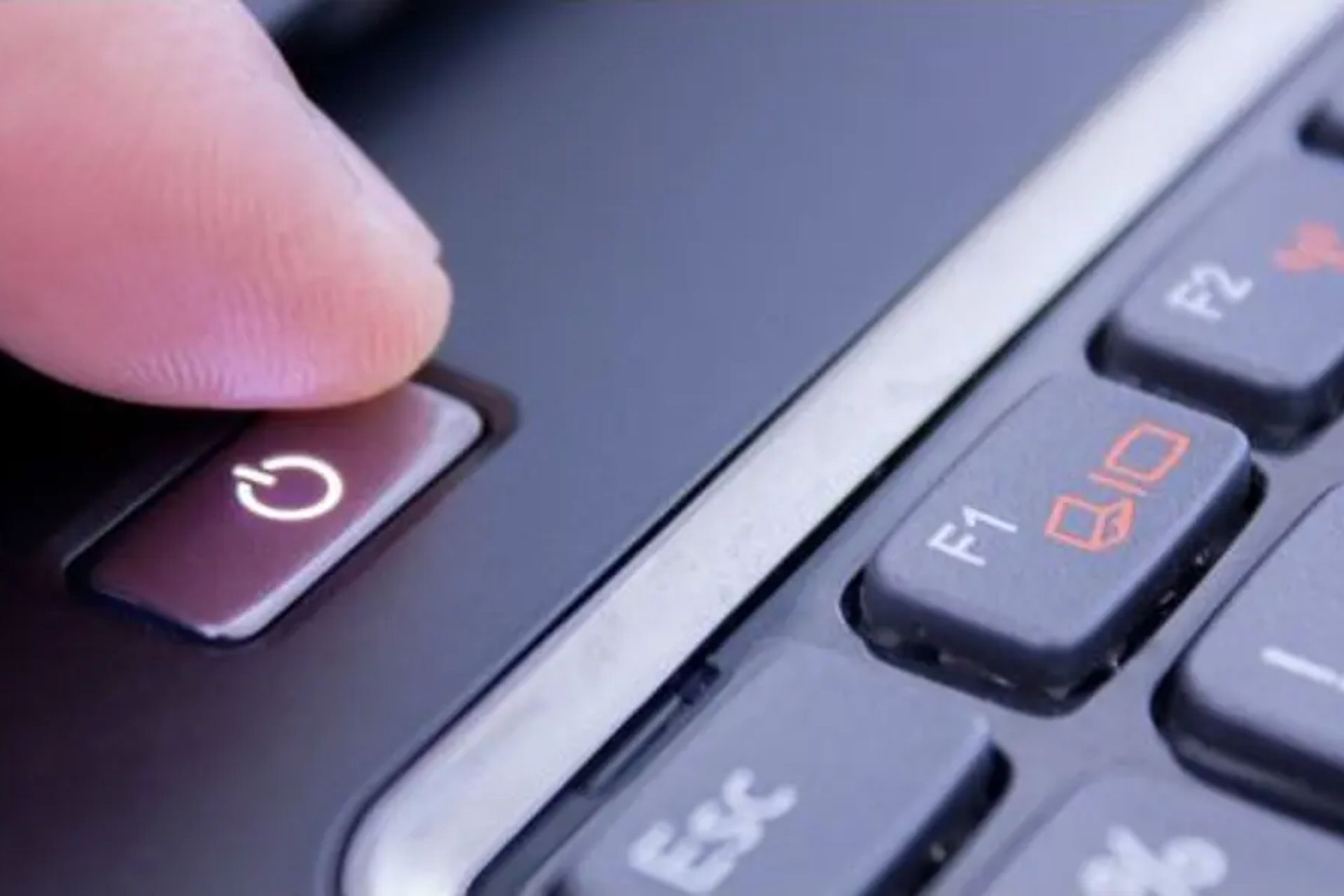

Press and hold power button for 30 seconds
While battery and power are disconnected, press and hold the power button for 30 seconds. This releases any remaining electrical charge from components like the RAM and BIOS.
Reconnect battery and power cord
Insert battery back into the laptop if applicable, plug the power adapter back in, and attempt to turn on the laptop as normal.
Step 3: Check for BIOS Issues
The BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) controls communication between the laptop’s OS and hardware. Corrupted BIOS settings can prevent the machine from powering on properly.
Access the BIOS menu
The method to enter BIOS setup varies by manufacturer and laptop model. Most commonly it involves pressing the Delete, F2, or Esc key repeatedly on bootup. Consult your device’s manual for the exact keys to access BIOS.
Examine BIOS for abnormal settings
Once in the BIOS menu, look for anything out of the ordinary. Be on the lookout for unfamiliar boot order settings, changed hardware presets, or error messages.
Reset BIOS to factory default settings
If you notice odd BIOS parameters but aren’t sure of the correct values, resetting to factory defaults should clear any problematic customizations. Refer to your manual for the proper reset procedure.
Step 4: Consider Hardware Issues
If you’ve tried all the basic troubleshooting to no avail, it’s likely an internal hardware component that has failed or become disconnected. Some possibilities include:
Overheating
Check that the laptop’s cooling vents aren’t obstructed by dust buildup or external objects. Thermal shutdown to prevent overheating is a protective mechanism in many laptops. A system that feels abnormally hot may indicate this safety trigger has been flipped.
Faulty RAM modules
Bad RAM can cause startup issues and power instability. For experienced users, reseating the RAM or testing each module individually can help diagnose this.
CMOS battery failure
The CMOS battery provides continuous low power to keep BIOS settings saved. If it’s depleted, settings may become erased or unstable.
Dislodged internal power connectors
With impact or drops, the small connectors supplying power from board to board can come loose. This requires dismantling the laptop to reseat cables.
Damaged motherboard
In worst case scenarios, the motherboard itself containing core logic components may be damaged. This requires professional service to replace or repair.
When to Seek Professional Help
If you’ve exhausted all the DIY troubleshooting tips above with no change, the laptop likely needs service from a qualified repair technician. They have the skills and equipment to diagnose issues like:
- Faulty power jacks
- Fried motherboards
- Short circuits
- Screen display failures
Seeking professional assistance is especially prudent if you’ll be:
- Disassembling the laptop extensively
- Replacing major components like the motherboard
- Making electrical continuity measurements
- Working with high voltage AC adapters
Technicians have the proper tools and training to avoid damage or accidental electric shock when dealing with the sensitive internals of laptops. For anything beyond basic external troubleshooting, it’s best to leave it to the professionals!
Don’t Despair, Your Laptop Can be Saved!
While a perfectly blank laptop screen is disheartening, don’t give up hope just yet. Carefully working through these troubleshooting techniques should reveal what’s preventing your device from turning on properly. With some fundamental checks of the AC adapter, battery, BIOS settings and internal hardware, you can get to the bottom of most startup issues.
Always exercise caution when working with electrical devices yourself. Seeking professional assistance is recommended if you’re unsure or uncomfortable with any of the steps outlined. With persistence and care, your laptop can pull through and get back to being your helpful digital companion once more!















Add Comment