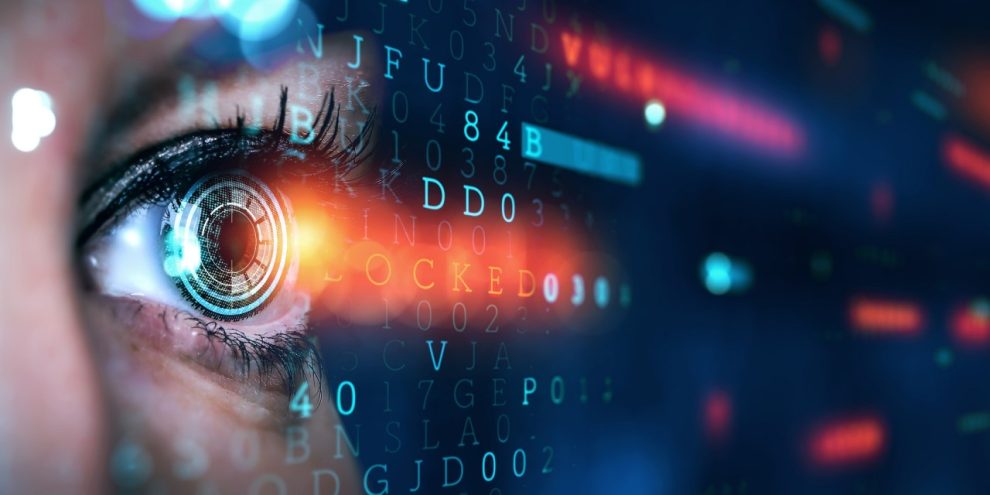
Computer vision, a captivating field within artificial intelligence, empowers machines to perceive and comprehend the visual world. It’s like granting computers the gift of sight, enabling them to analyze images and videos, extract meaningful information, and even interact with their surroundings in visually intelligent ways.
Here’s a closer look at this remarkable technology:
Key Concepts and Techniques
Image Processing: The foundation of computer vision lies in processing raw image data, enhancing quality, and extracting relevant features using techniques like filtering, edge detection, segmentation, and compression.
Object Recognition and Classification: Algorithms learn to identify objects within images or videos, categorize them based on learned features, and even detect their position and orientation within a scene.
Facial Recognition: Specialized algorithms pinpoint faces in images and videos, compare them to known faces, and even analyze facial expressions to gauge emotions and attention.
Motion Tracking: Computer vision can track the movement of objects or people within videos, enabling applications like self-driving cars, surveillance systems, and immersive virtual experiences.
Real-World Applications
Medical Imaging: Computer vision assists radiologists in analyzing medical images, detecting tumors, lesions, and other abnormalities with greater accuracy and speed.
Autonomous Vehicles: Self-driving cars rely heavily on computer vision to perceive their surroundings, detect obstacles, and navigate safely.
Security and Surveillance: Computer vision powers facial recognition systems for security purposes, monitors public spaces for suspicious activity, and even tracks objects in real-time for traffic management.
Image Search and Social Media: Efficient image retrieval and categorization enhance search engines and social media platforms, enabling users to find relevant content effortlessly.
Robotics: Robots equipped with computer vision can navigate environments, manipulate objects, and even interact with humans in more intuitive ways.

Challenges and Opportunities
Complexities of Visual Perception: Replicating the human visual system’s versatility and adaptability remains a challenge.
Data Dependency: Computer vision algorithms require vast amounts of labeled training data to achieve high accuracy, often posing challenges in data collection and annotation.
Bias and Fairness: Algorithms can perpetuate biases if trained on biased datasets, raising ethical concerns and necessitating careful attention to data diversity and inclusion.
Explainability and Transparency: Understanding how computer vision algorithms make decisions is crucial for trust and accountability, but often remains a challenge due to their complex nature.
The Future of Seeing Machines
Advanced Algorithms: Research continues to develop more sophisticated algorithms capable of handling complex visual tasks, understanding context, and adapting to new situations.
Edge Computing: Bringing computer vision capabilities to devices themselves, enabling real-time processing and reducing reliance on cloud infrastructure.
Human-AI Collaboration: Combining human expertise with computer vision’s efficiency can lead to more robust and reliable systems.
Ethical Development: Prioritizing fairness, transparency, and responsible use of computer vision technologies is essential to ensure they benefit society equitably.
Computer vision is poised to transform numerous industries and aspects of our lives. By addressing its challenges and embracing ethical development, we can harness its power to create a world where machines not only see but also understand, learn, and interact with the visual world responsibly, shaping a future of enhanced safety, efficiency, and understanding.














Add Comment