When your Windows computer starts acting up with sluggish performance, unresponsive programs, or mysterious resource consumption, Task Manager is the go-to tool for diagnosing and resolving these issues. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll walk you through the process of opening Task Manager, explore its various features and functionalities, and share practical troubleshooting tips to help you optimize your system’s performance.
Throughout this guide, the phrase “open Task Manager” refers to the act of launching the built-in Windows utility that provides detailed information about your computer’s running applications, processes, and system resources.
The Benefits of Using Task Manager
Before we dive into the specifics of opening Task Manager, let’s take a moment to understand why this tool is so valuable for every Windows user:
- Identify resource hogs: Task Manager provides real-time data on CPU, memory, disk, and network usage, allowing you to pinpoint which applications or processes are consuming the most resources and potentially causing performance bottlenecks.
- Terminate unresponsive programs: When an application freezes or becomes unresponsive, Task Manager allows you to end the associated task, freeing up system resources and potentially resolving the issue.
- Monitor system performance: Keep tabs on your computer’s overall health by monitoring CPU usage, memory consumption, disk activity, and network performance in real-time.
- Control startup programs: Task Manager lets you manage which applications automatically launch when you start your computer, helping you improve boot times and prevent unnecessary programs from consuming resources in the background.
- Access detailed system information: Task Manager provides quick access to in-depth information about your system, such as the operating system version, processor details, and installed memory.
By leveraging these benefits, you can use Task Manager to diagnose performance issues, optimize resource allocation, and gain valuable insights into your system’s overall health.

Opening Task Manager: Multiple Methods for Easy Access
Windows offers several ways to open Task Manager, catering to different preferences and situations. Let’s explore the most common methods:
Method 1: Keyboard Shortcut (Fastest)
The quickest and most widely used method to open Task Manager is via a simple keyboard shortcut:
- Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc simultaneously on your keyboard.
- Task Manager will immediately open, regardless of which application or screen you’re currently using.
Method 2: Right-Click the Taskbar
Another convenient way to access Task Manager is through the Windows taskbar.
- Right-click anywhere on the taskbar, typically located at the bottom of your screen.
- From the pop-up menu, select “Task Manager.”
- Task Manager will open, providing access to its various tabs and features.
Method 3: Start Menu or Search Bar
You can also open Task Manager through the Start menu or the search bar, depending on your Windows version.
- Windows 10 and 11: Click the Start menu icon (usually in the bottom-left corner of the screen), type “task manager” in the search bar, and click on the “Task Manager” result.
- Windows 8.1: Right-click the Start menu icon and select “Task Manager” from the pop-up menu.
Method 4: Windows Security Screen
While less common, you can access Task Manager through the Windows Security screen:
- Press Ctrl + Alt + Delete simultaneously on your keyboard.
- On the Windows Security screen, click “Task Manager” or “More details” (depending on your Windows version).
- Task Manager will open, ready for you to explore its features and functionalities.
Note that some methods, like the Ctrl + Shift + Esc shortcut, may not work in certain remote desktop environments. If you encounter issues, consult your remote desktop software documentation for alternative methods to open Task Manager.
Navigating the Task Manager Interface
Once you’ve successfully opened Task Manager, it’s essential to understand its various tabs and the information they provide. Let’s take a closer look at each tab:
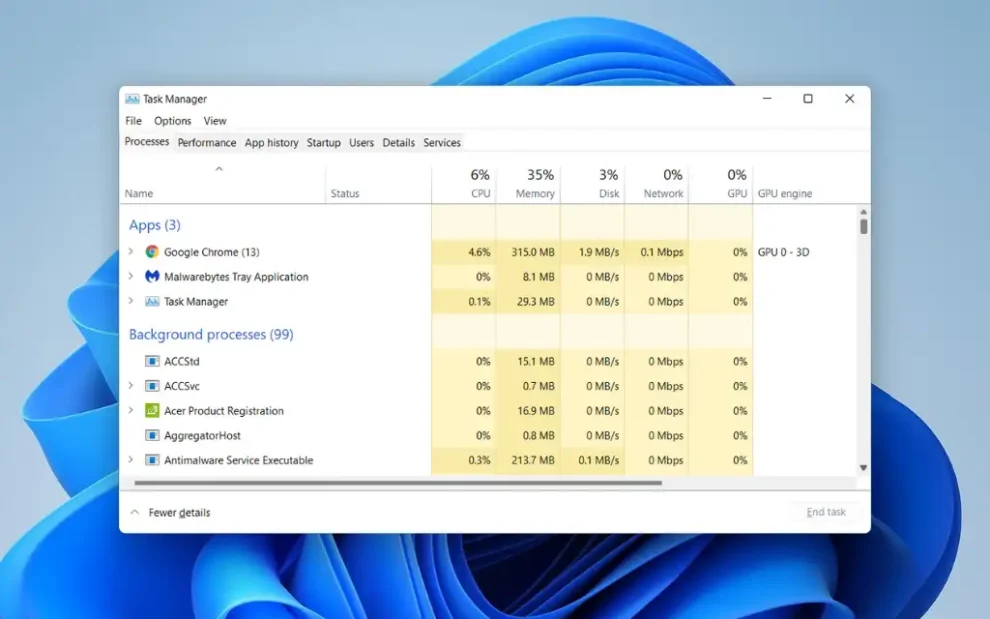
Processes Tab
The Processes tab is the default view when you open Task Manager. It displays a list of all running applications and background processes, along with their respective CPU, memory, disk, and network usage. You can:
- Sort the list by any column to identify resource-intensive processes quickly.
- Right-click on a process and select “End task” to terminate unresponsive programs.
- View additional details about a process by right-clicking and selecting “Properties” or “Open file location.”
Performance Tab
The Performance tab provides real-time graphs and data on your system’s overall resource usage, including:
- CPU usage and speed
- Memory usage and allocation
- Disk activity and transfer rates
- Network utilization and link speed
This tab is particularly useful for identifying performance bottlenecks and monitoring your system’s health over time.
App History Tab (Windows 11)
Exclusive to Windows 11, the App History tab displays the historical resource usage of applications over time. This information can help you identify apps that consistently consume significant resources, even when they’re not actively in use.
Startup Tab
The Startup tab lists all the applications configured to launch automatically when you start your computer. You can:
- View the impact of each startup program on your boot time.
- Disable unnecessary startup programs by right-clicking and selecting “Disable.”
- Enable previously disabled startup programs by right-clicking and selecting “Enable.”
Managing your startup programs can significantly improve your system’s boot time and overall performance.
Users Tab (Not Available on Windows 11 Home)
The Users tab displays information about currently logged-in users and their associated processes. You can:
- View the resource usage of each user’s processes.
- Switch between users or log off a specific user.
- End tasks associated with a particular user’s processes.
This tab is particularly useful for managing multi-user environments or troubleshooting user-specific issues.
Details Tab
The Details tab provides a more advanced and granular view of running processes compared to the Processes tab. It includes information such as:
- Process ID (PID)
- Process status and priority
- CPU usage per core
- Memory usage details
This tab is primarily intended for advanced users who require in-depth process information for troubleshooting or monitoring purposes.
Services Tab (Not Available on Windows 11 Home)
The Services tab lists all the background services running on your system. These services are essential for various system functions and features. You can:
- View the status and description of each service.
- Start, stop, or restart services (caution recommended).
- Open the Services desktop app for advanced service management.
Exercise caution when managing services, as stopping or disabling critical services can lead to system instability or functionality loss.
Task Manager Troubleshooting Tips
Now that you’re familiar with Task Manager’s interface and features, let’s explore some practical troubleshooting tips to help you optimize your system’s performance:
- Identify and terminate resource-hungry processes. If your computer feels sluggish, sort the Processes tab by CPU, memory, disk, or network usage to identify processes consuming excessive resources. End tasks associated with unresponsive programs or investigate further if a legitimate application seems to be misbehaving.
- Manage startup programs: Disable unnecessary programs from launching at startup using the Startup tab. Focus on disabling programs you rarely use or those that don’t require immediate startup. This can significantly improve your system’s boot time and overall performance.
- Monitor system performance trends: Use the Performance tab to keep an eye on your system’s resource usage over time. Identify patterns or spikes in CPU, memory, disk, or network usage that may indicate underlying hardware or software issues.
- Investigate user-specific issues: If you’re experiencing issues with a specific user account, use the Users tab (when available) to identify and manage processes associated with that user. This can help you isolate and resolve user-specific problems.
- Consult online resources and documentation: For more advanced troubleshooting, refer to online forums, official Microsoft support articles, or technical documentation specific to the processes or services you’re investigating.
By regularly using Task Manager and applying these troubleshooting tips, you can proactively monitor your system’s health, identify potential issues, and take appropriate actions to optimize performance.
The Future of Task Manager
As Windows continues to evolve, so does Task Manager. Microsoft is continuously working on enhancing this essential system utility to provide users with even more powerful tools for managing and optimizing their computers. Some potential future developments include:
- Enhanced performance monitoring: Expect to see more granular and user-friendly performance monitoring features, providing deeper insights into resource allocation and utilization.
- Integration with system settings: Task Manager may become more seamlessly integrated with Windows system settings, allowing users to manage startup programs, services, and other performance-related options more easily.
- AI-powered optimization: As artificial intelligence (AI) technologies advance, we may see the integration of AI-powered suggestions and optimizations within Task Manager, helping users identify and resolve performance bottlenecks more effectively.
As these exciting developments unfold, we’ll be sure to update this guide to keep you informed and equipped with the latest Task Manager tips and tricks.
Conclusion
Task Manager is a powerful and indispensable tool for every Windows user, providing a wealth of information and functionality for managing, troubleshooting, and optimizing your system’s performance. By understanding how to open Task Manager, navigate its interface, and apply practical troubleshooting tips, you can take control of your computer and ensure it runs at its best.
Remember to regularly monitor your system’s performance using Task Manager, proactively address resource-hungry processes, manage startup programs, and stay informed about the latest best practices and future enhancements to this essential Windows utility.
Armed with the knowledge and skills shared in this guide, you’re now ready to tackle performance issues head-on and keep your Windows computer running smoothly. Happy troubleshooting!















Add Comment