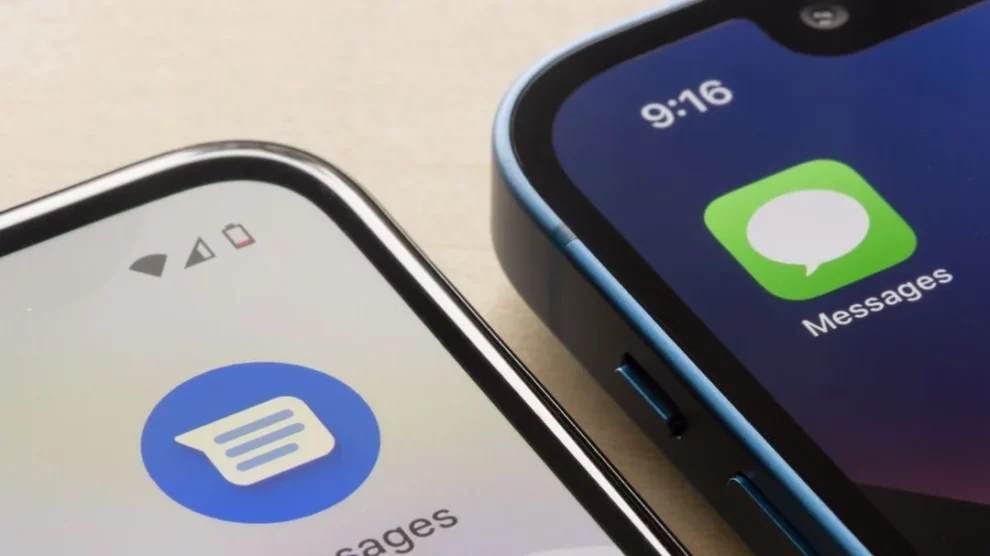
Apple’s recent adoption of RCS messaging technology has drawn criticism from security experts and industry analysts, who argue that the company’s implementation falls short of meaningful cross-platform security improvements. The move, while appearing to bridge the long-standing messaging divide between iOS and Android devices, has left crucial security vulnerabilities unaddressed.
According to security specialists, the heart of the problem lies in how messages are handled between different platforms. While iPhone-to-iPhone communications remain secure through iMessage, and Android-to-Android chats maintain protection through Google’s encryption implementation, cross-platform messaging between iOS and Android devices continues to lack essential security safeguards.
The FBI has expressed concerns about these security gaps, highlighting how the current implementation could leave users vulnerable to potential privacy breaches. The situation is particularly troubling given the increasing importance of mobile messaging in both personal and professional communications.
At the core of this security dilemma is RCS (Rich Communication Services) technology itself. The current open standards for RCS do not include native encryption support, leaving a significant security void in cross-platform messaging. While Google has proactively addressed this limitation by implementing its own encryption for Android-to-Android communications, Apple’s basic RCS implementation adheres strictly to the standard protocol, without additional security enhancements.
Security experts point out that this technical limitation didn’t have to become a practical problem. Apple and Google could have collaborated to develop a unified encryption standard for cross-platform messaging, similar to how other messaging platforms handle secure communications. Instead, the current implementation maintains the status quo of unsecured cross-platform messaging, merely dressed up in new technological clothing.
The implications of this security gap extend beyond simple text messages. As mobile communications increasingly serve as a primary channel for sensitive personal and business information, the lack of robust encryption in cross-platform messaging poses significant risks. Users sharing confidential information between iOS and Android devices may unknowingly expose their communications to potential security threats.
Google’s approach to RCS security demonstrates that technical solutions are possible. The company has successfully implemented encrypted RCS messaging between Android devices and through Chrome browsers connected to Android phones. This implementation shows that securing RCS communications is technically feasible, making Apple’s basic implementation appear even more conspicuous in its limitations.
Industry observers suggest that Apple’s approach to RCS reflects a broader pattern in the company’s ecosystem strategy. By maintaining a clear distinction between the security of in-platform versus cross-platform messaging, Apple creates an implicit incentive for users to stay within its ecosystem, where communications are fully secured through iMessage.
The situation highlights a growing tension in the mobile industry between platform-specific advantages and universal user security. While companies naturally seek to differentiate their products and services, the increasing interconnectedness of modern communications demands a more collaborative approach to security implementation.
Consumer advocacy groups argue that this scenario exemplifies how corporate strategies can sometimes overshadow user interests. The decision to implement basic RCS without enhanced security features effectively prioritizes ecosystem control over universal user protection, leaving millions of cross-platform communications vulnerable.
Looking forward, the resolution to this security challenge will likely require either industry collaboration or regulatory intervention. As messaging continues to evolve as a critical communication infrastructure, the pressure to establish universal security standards may eventually outweigh individual corporate interests.
Until then, users engaging in cross-platform messaging between iOS and Android devices should remain aware of the security limitations and consider alternative messaging platforms for sensitive communications. The situation serves as a reminder that technological progress without meaningful security improvements may create an illusion of advancement while leaving fundamental vulnerabilities unaddressed.
The current state of cross-platform messaging security underscores a broader challenge in the tech industry: balancing competitive advantages with user protection. As users increasingly demand seamless and secure communication across all platforms, companies will need to reconsider whether minimal compliance with standards truly serves their long-term interests and those of their users.













Add Comment