In a move poised to transform the very essence of logistics and last-mile delivery, e-commerce titan Amazon has pulled off a feat once dismissed as science fiction – unveiling a fully operational drone delivery service set to take ecommerce fulfillment to unprecedented new heights. Literally.
Brace yourself as we soar into the uncharted skies where Amazon Develops Drone Delivery Service, Reshaping Logistics and every facet of how we receive goods. This is no mere gimmick, but a revolutionary paradigm shift in supply chain management that could have seismic ramifications across industries. Prepare for a future where your packages arrive by air, ferried across cities and suburbs by unmanned aerial vehicles on a scale once unimaginable.
What is Amazon’s Drone Delivery Service?

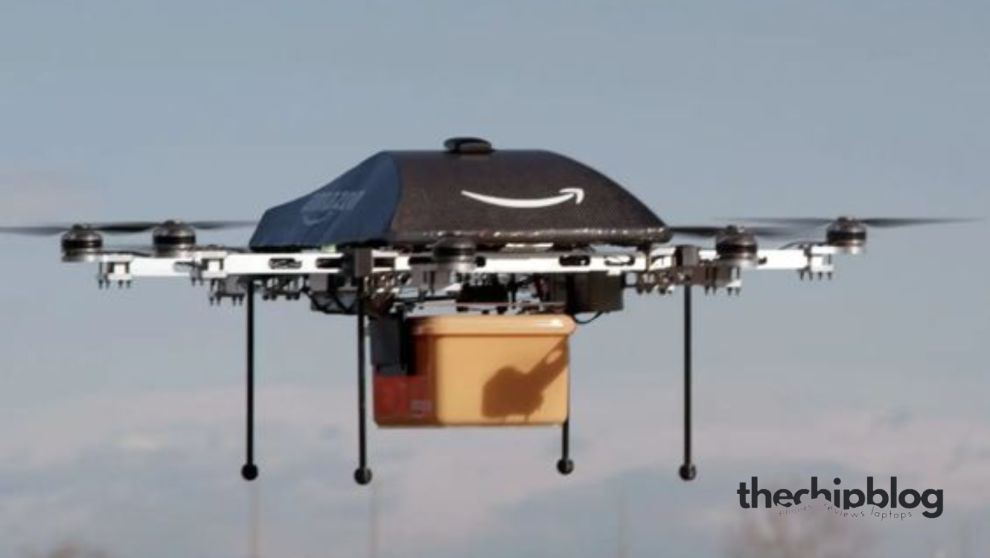
After years of research, development, and regulatory hurdles, Amazon has officially unleashed its “Prime Air” drone delivery service – an unmanned logistics operation precisely engineered to deliver packages up to 5 pounds to customers in 30 minutes or less utilizing autonomous drones.
The service deploys specialized hexagonal drones with a hybrid design blending elements of helicopters and fixed-wing aircraft. With six propellers enabling vertical take-off and landing plus two front rotors for extended horizontal flight, these delivery robots can operate from centralized air terminals serving broad metro areas within a 7.5-mile radius.
Utilizing robust sensor arrays, artificial intelligence, and machine learning models, Amazon’s delivery drones are designed to navigate complex urban environments at altitudes under 400 feet while safely avoiding obstacles and other air traffic.
Each drone incorporates a securely locking package compartment that automatically opens during the final delivery descent. Parcels are then gently lowered via a tether system to customers’ yards, patios, or specified locations – eliminating the need for neighborhood truck routes or doorstep drop-offs.
Prime Air service is initially launching in select cities and suburbs across the United States and United Kingdom, with plans for rapid expansion into other markets as regulatory approvals and infrastructure build-outs progress. It represents Amazon’s first major foray into autonomous aerial logistics and their boldest bid yet to revolutionize the ecommerce fulfillment model.
How Do Amazon’s Delivery Drones Work?
While the concept may seem futuristic, the underlying mechanics and technology enabling Amazon’s autonomous drone-based delivery operations draw upon a sophisticated synthesis of existing aerospace, robotics, and artificial intelligence innovations. Here’s a high-level breakdown of the core systems:
Hexagonal Hybrid Design: The distinctive hexagonal shape combines maneuverability and speed. Six propellers provide vertical lift for take-off and landing, while two forward propellers enable sustained forward flight once airborne. The aerodynamic body minimizes drag and wind shear for extended range up to 15 miles.
Redundant Propulsion and Avionics: Every component from motors and batteries to GPS, communications, and guidance systems maintain redundant failover backups. If any aspect fails, the drone can still navigate and land safely.
Sensor Fusion: A diverse array of visual, thermal, lidar, ultrasonic, and other environmental sensors feed into machine learning models allowing drones to precisely map their surroundings and detect obstacles like buildings, trees, power lines, birds, and other aircraft.
Autonomous Flight and Navigation: Relying on advanced guidance systems and artificial intelligence, the drones plan optimized delivery routes accounting for airspace constraints, weather patterns, and no-fly zones while dynamically re-routing around spontaneous hazards and updating in real-time based on sensor data.
Computer Vision and Machine Learning: Sophisticated CV and ML models enable functions like automated landing zone identification and precision delivery without human intervention. Drones can safely place packages on specified targets like patios or lawns while avoiding obstacles.
Hybrid Power: Redundant lithium battery packs provide up to 30 minutes of flight time, while heated body panels allow operation in cold climates. The hybrid fixed-wing design is optimized for efficient range and speed during horizontal transit.
Secure Package Compartment: An anti-collision exterior shell protects the interior cargo compartment that locks securely until reaching the delivery location and gently lowering the package via tether during descent.
Weather Hardening: Designs account for precipitation, wind gusts, and challenging conditions through robust waterproofing, anti-icing elements, and sensors optimized for visibility through rain, fog, and other atmospheric disturbances.
Traffic Management and Air Control: A centralized air traffic control system monitors all drones, sharing data with local aviation authorities to maintain safe integration with airspace systems, while routing drones to avoid collisions even in concentrated metro areas.
While exceptionally complex under the hood, the drone’s operation is elegantly simple for customers – order on Amazon and your package could arrive via an autonomous aerial robot in under 30 minutes. It’s a seamless experience that could make truck-based delivery seem curiously antiquated by comparison.
How is Amazon’s Drone Delivery Service Different?
Countless startups and industry giants from Google to UPS have previously announced or experimented with drone delivery concepts, so what separates Amazon’s offering from these earlier initiatives? A few key differentiating factors:
Scale and Infrastructure: Leveraging its vast logistics empire and engineering resources, Amazon has built an entire comprehensive drone delivery ecosystem from the ground up – encompassing everything from air traffic control and routing systems to drone design, manufacturing, maintenance, and charging infrastructure. They can deploy and operate at a scale no startup can match.
Complete Vertical Integration: Amazon controls the entire experience end-to-end from online ordering and warehousing through local air terminals directly serving customers. Drones are deployed from local facilities rather than remote drops, ensuring efficient last-mile delivery.
Regulatory Stamps: After years of work with the FAA and international aviation authorities, Amazon has secured regulatory approvals allowing broader deployment of their drones within specified operational parameters – greenlighting major commercial expansion.
Hybrid Drone Design: Employing a unique hybrid vertical take-off to horizontal transition configuration, Amazon’s drones blend the speed and range of winged aircraft with the precision hover and landing capabilities of multi-rotor drones. The hexagonal design also provides redundancy.
Machine Learning Competency: Few companies outside the military/aerospace realm possess Amazon’s deep expertise in autonomous robotic systems. Their proficiency in artificial intelligence and machine learning is instrumental in enabling complex urban autonomous drone navigation.
First Mover Advantage: By rolling out Prime Air first at scale, Amazon gains a major time-to-market lead over rivals still in earlier testing stages. Commercializing the concept quickly is key to establishment.
Vertical integration across the entire ecosystem, Amazon can rapidly expand delivery service availability coupled with sophisticated autonomy systems combing robust industrial drones with machine learning software savvy. It’s a powerful competitive advantage over alternative drone delivery efforts that remain mere pilots.
What are the Benefits of Drone Delivery?

While Amazon’s drone delivery service may seem novel or even gimmicky on the surface, it provides very real operational advantages and consumer benefits compared to traditional truck-based fulfillment:
Blazing Fast Delivery Speed: With drones capable of dropping off packages in 30 minutes or less, Prime Air can dramatically accelerate delivery timeframes for ideal locations – potentially offering same-hour courier speeds for a fraction of the cost. For perishable items or urgent needs, it’s a game-changer.
Reduction in Delivery Costs: Once infrastructure and initial capital costs are absorbed, drones offer significant cost-savings over truck fleets by eliminating fuel, vehicle maintenance, insurance, and most critically – driver labor expenses. Automated aerial drones could reduce costs per delivery by 50% or more.
Hyper-Local Fulfillment Hubs: Drone operations can be dispersed across ultra-local terminals within neighborhoods and suburbs, shortening delivery routes. This allows inventory pooling closer to customers versus centralized warehouses on city peripheries.
Increased Throughput and Capacity: Autonomous drones flying optimized routes with machine precision can complete more deliveries per vehicle load compared to human drivers navigating traffic and finishing routes. Localized aerial drone capacity ultimately scales better.
Lower Carbon Footprint: Compared to delivery trucks idling in traffic or driving increasingly circuitous routes, drones consume minimal energy and generate negligible emissions. Their environmental impact has significantly less ecological implications.
Improved Network Reliability: Aerial drone swarms are less susceptible to interruptions like vehicle breakdowns, accidents, weather hazards, traffic jams, and other issues plaguing conventional ground-based delivery fleets.
Contactless Drop-Offs: In today’s environment, reducing human-to-human contact is a valued safety benefit for residential deliveries that drones easily address.
Enhanced Accessibility: Drones could potentially reach remote or underserved locations traditional last-mile delivery finds logistically challenging, enabling greater equity.
While drone delivery may seem frivolous for some items, the transformative implications could fundamentally alter the economics and efficiencies of ecommerce fulfillment in ways that empower faster, cheaper, and more sustainable shipping at scale.
What are the Potential Drawbacks of Drone Deliveries?

For all their revolutionary promise, Amazon’s Prime Air drone delivery service is not without limitations, concerns, and drawbacks that must be carefully addressed as operations expand:
Public Safety Hazards: Rogue drones striking vehicles, pedestrians, or property could be catastrophic. Ensuring foolproof reliability and air traffic control is paramount. Battery failures, hackers, technical glitches, or mechanical malfunctions also pose risks requiring robust failsafes.
Environmental Impact: While emissions and energy use may be less than conventional trucks, operating large-scale drone fleets still bears an environmental footprint warranting examination of noise pollution, wildlife impacts, land use implications for air terminals, and lifecycle materials demands.
Privacy and Security Concerns: Thousands of autonomous drones equipped with sensors and cameras routinely buzzing over populated areas give rise to public fears around privacy erosion, surveillance, or misuse for nefarious purposes warranting stringent data governance.
Regulatory Burdens: Gaining approvals to launch Prime Air was arduous, but maintaining regulatory compliance as operations rapidly scale and transform urban airspaces will require extensive coordination with aviation authorities domestically and globally.
Community Acceptance: While convenient for customers, residents may rebel against constant drone flyovers and noise in their communities – especially concentrated around air terminal hubs. Building public acceptance is key.
Vulnerability to Legislative Bans: Well-organized lobbying efforts or sensationalized public incidents could prompt reactionary bans or restrictions on drone operations halting progress much like ridesharing faced city-by-city legislative challenges.
Infrastructure and Scalability Limits: Ramping a vast decentralized network of regional drone air terminals, charging stations, command centers, and other ground infrastructure entails massive capital costs and operational complexities potentially stunting growth.
Job Disruption: Advances in autonomous delivery automation from drones to robots could significantly erode human delivery driver employment over time, warranting proactive workforce reskilling and economic disruption mitigation.
While remarkable, Amazon isn’t operating in a vacuum – addressing public anxieties and unintended consequences around wide-scale drone operations will be critical to maintaining societal support and acceptance as their unmanned flying fleet increasingly saturates urban skies.
What is Amazon’s Competitive Edge with Drones?
As transformative and convenient as drone delivery may seem, Amazon will face stiff competition as rivals like Walmart, UPS, FedEx, and others inevitably roll out their own autonomous aerial services. So what advantages does Amazon’s Prime Air maintain over other commercial drone efforts?
Massive Fulfillment Footprint: Amazon’s colossal existing fulfillment infrastructure from warehouses to shipping hubs provides an enormous foundation from which to build localized drone air terminals, whereas competitors must create these networks from scratch.
End-to-End Integration: As an ecommerce retailer already managing every delivery step, Amazon can integrate drone operations into its existing logistics ecosystem with minimal disruption. Ground carriers must fundamentally reorient operations.
Machine Learning Leadership: Few companies globally possess Amazon’s deep experience developing and deploying artificial intelligence systems at scale – a core competency critical for safe autonomous drone navigation in complex environments.
Cloud Infrastructure: Leveraging its AWS cloud platform, Amazon can readily provision data streams, storage, and processing horsepower necessary for managing multitudes of delivery drones remotely in regional air spaces.
Existing Drone Tech R&D: Amazon’s Prime Air program builds upon nearly a decade of internal drone prototyping, reliability engineering, and drone systems integration – giving them extensive head start validating the technology.
Capital Resources: With the financial wherewithal to invest billions into building autonomous drone delivery at scale globally, cost is less prohibitive to Amazon for establishing critical infrastructure.
Prime Loyalty: Over 200 million Prime subscribers provide a captive audience incentivized to leverage the drone delivery service integrated into Amazon’s ecommerce ecosystem – a built-in base for adoption no rival can match.
Branding Innovation: As an ecommerce pioneer, Amazon already possesses a brand image as an innovator consumers associate with cutting-edge solutions like drone delivery. Competitors may be perceived as lagging.
The tech titan’s massive ecommerce scale and customer base, machine learning capabilities, financial resources, brand mindshare, and end-to-end integration of its logistics ecosystem gives Amazon a significant competitive moat – albeit one that won’t remain unchallenged for long by rivals if drone delivery takes flight as projected.
What are the Future Applications of Drone Delivery?
While Prime Air unveils Amazon’s grand entrance into drone delivery, the implications extend far beyond mere ecommerce shipping if autonomous aerial logistics mature as anticipated. Here are some of the most compelling future applications we may see:
Emergency Management: Drones could revolutionize emergency response by rapidly shuttle medical supplies, equipment, PPE, water, food, and more to impacted areas after natural disasters when traditional transportation is interrupted. The pandemic highlighted urgent needs.
Humanitarian Aid and Relief: Similarly, aid organizations could leverage drone fleets for contactless delivery of humanitarian provisions and supplies to remote or logistically-inaccessible locations impacted by conflict or crisis.
Just-in-Time Logistics: Manufacturers and retailers may utilize drone services to enable radically streamlined “just-in-time” inventory replenishment, circumventing supply chain chokepoints and eliminating costly warehousing and surplus buffers.
Infrastructure Oversight: Deploying drones to inspect remote infrastructure like pipelines, power line corridors, and cellular towers expediently could improve maintenance and accelerate repairs.
Environmental Monitoring: Ecologists and conservationists could use drones to access hard-to-reach areas for environmental surveys, wildlife tracking, anti-poaching patrols, and other environmental protection initiatives.
Agriculture and Food: From crop-spraying and water delivery to planting and harvesting in hard-to-reach areas, drone logistics could enhance farming efficiency and boost crop yields globally.
Search and Rescue: Ability to deploy drone swarms quickly over wilderness areas or disaster debris could significantly enhance locating missing persons or victims requiring remote rescue.
Defense and Security: Military applications could leverage drone logistics for supply drops, reconnaissance, weapons deployment, and other strategic operations too dangerous or difficult for manned missions.
While still commercially in its infancy, the underlying technological foundation enabling Amazon’s drone delivery service ushers in an exciting new era of efficient, scalable, and distributed unmanned logistics automation with profound implications far beyond mere ecommerce shipments. For developing economies, natural disasters, or wherever traditional transportation is inadequate, autonomous drone logistics could become an existential lifeline.
What Regulatory Challenges Does Amazon Face?

For all its groundbreaking innovation, Prime Air’s drone delivery service hasn’t been immune to regulatory scrutiny or hurdles around safety and compliance. Before expanding globally, Amazon faces key challenges around:
Airspace Integration: While permitted operation in US and UK low-level airspaces currently, gaining approval for nationwide scaling and integration within broader air traffic control requires extensive evaluation of procedures, reliability, and communication protocols to confirm safety.
Privacy and Surveillance Restrictions: Amid increasing public concerns, lawmakers may impose restrictions around allowable camera use, acoustic sensors, and data gathering to protect privacy for deliveries over residential areas.
Licensing and Certification: Legally certifying Amazon’s complex autonomous drone systems, fleet licensing, and remote pilot licensing across jurisdictions is a patchwork requiring proactive coordination with varied oversight bodies like the FAA.
Community Noise and Nuisance Laws: Localized ordinances governing noise pollution and public nuisances could prompt restrictions on densities, operating hours, and areas where drone activity is permitted around neighborhoods depending on community sentiment.
Environmental Impact Assessments: Amazon may face requirements for environmental impact studies and public comment periods examining the ecological implications of widespread drone operations in areas intersecting national parks, wilderness preserves, and sensitive habitats.
Liability Frameworks: If drones malfunction and cause property damage or injury, establishing equitable liability frameworks, insurance regimes, and accident investigation protocols remain areas requiring regulatory clarity to adequately mitigate risks.
Federal Preemption Battles: While the FAA governs national airspace, cities and states may still attempt localized rules and restrictions prompting potential federal preemption battles over jurisdiction as drone operations become ubiquitous.
Crossing Borders: For international integration, Amazon must coordinate compliance across patchworks of varied sovereign national and regional drone regulations with differing vehicular remote pilot, privacy, and operational requirements.
While scaling Prime Air domestically remains the priority, Amazon recognizes regulatory harmonization and public acceptance are vital to expanding drone delivery’s global footprint. As the pioneer, they’ll set standards other commercial drone operators must follow – both boon and burden.
What’s Next for Drone Delivery Expansion?
Amazon’s launch of Prime Air drone delivery service may be a milestone moment, but it’s merely the first step in a much grander vision toward transforming logistics and transportation through extensive autonomous aerial networks:
Evolving Drone Designs: As the technology matures, expect increasingly sophisticated purpose-built drone models tailored for specific payloads and missions. Scaled down versions for smallerpackages or larger drones capable of heavier cargo are already in R&D.
Drone Superhighways: To accommodate high-volume traffic between densely populated areas and logistics facilities, Amazon may designate dedicated aerial “superhighway














Add Comment