Organizations of all sizes face an increasing risk of cyberattacks. A well-crafted incident response plan is essential to mitigate the impact of security breaches and ensure a swift and effective recovery. This article provides a comprehensive template for developing a cybersecurity incident response plan, tailored to meet the specific needs of your organization.
1. Incident Identification and Reporting
- Define incidents: Clearly define what constitutes a security incident within your organization.
- Reporting procedures: Establish procedures for employees to report suspicious activity or suspected incidents.
- Designated contacts: Identify individuals responsible for receiving and triaging incident reports.
2. Incident Containment
- Isolation: Isolate affected systems or networks to prevent further damage.
- Network segmentation: Implement network segmentation to limit the spread of an attack.
- Temporary measures: Employ temporary measures, such as disabling affected services or blocking access to vulnerable systems.
3. Incident Investigation
- Forensic analysis: Conduct a thorough forensic investigation to gather evidence and identify the root cause of the incident.
- Data collection: Collect relevant data, such as system logs, network traffic, and employee activity.
- Incident timeline: Create a timeline of events to understand the sequence of the attack.
4. Incident Eradication
- Remove malware: Remove any malicious software from affected systems.
- Patch vulnerabilities: Apply security patches to address vulnerabilities exploited in the attack.
- Restore systems: Restore systems and data from backups, if necessary.
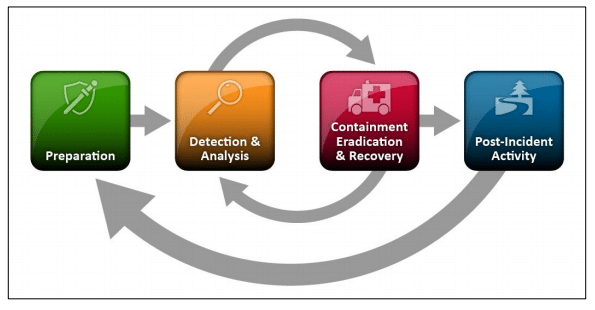
5. Incident Recovery
- Business continuity plan: Activate your business continuity plan to ensure essential operations continue.
- Data restoration: Restore critical data from backups.
- System restoration: Restore systems and applications to their pre-incident state.
6. Lessons Learned
- Post-incident review: Conduct a thorough review of the incident to identify lessons learned.
- Security improvements: Implement security improvements to prevent similar incidents from happening in the future.
- Training and awareness: Provide additional training and awareness to employees to enhance their security knowledge.
7. Communication and Notification
- Internal communication: Communicate with affected employees and stakeholders within the organization.
- External communication: Develop a plan for communicating with external stakeholders, such as customers, partners, and regulators, as necessary.
- Regulatory reporting: Comply with any regulatory requirements for reporting data breaches.
8. Testing and Maintenance
- Regular testing: Conduct regular incident response drills to test your plan and identify areas for improvement.
- Plan maintenance: Regularly review and update your incident response plan to reflect changes in your organization’s security posture.
Additional Considerations
- Third-party risk management: Include third-party vendors and suppliers in your incident response plan.
- Cloud security: Address cloud-specific security considerations, such as data encryption, access controls, and incident response in the cloud.
- Emerging threats: Stay informed about emerging threats and adjust your plan accordingly.
Example Incident Response Team Structure
- Incident commander: Oversees the incident response effort and makes critical decisions.
- Technical experts: Provide technical expertise and support.
- Legal counsel: Offers legal guidance and advice.
- Public relations: Handles communications with external stakeholders.
- Human resources: Assists with employee communications and investigations.
Best Practices for Incident Response
- Regular testing: Conduct regular incident response drills to ensure your plan is effective.
- Training and awareness: Provide ongoing training and awareness to employees to enhance their security knowledge.
- Third-party risk management: Evaluate the security practices of third-party vendors and suppliers.
- Cloud security: Address cloud-specific security considerations, such as data encryption, access controls, and incident response in the cloud.
- Emerging threats: Stay informed about emerging threats and adjust your plan accordingly.
By developing a comprehensive and well-tested incident response plan, organizations can mitigate the impact of cyberattacks and demonstrate their commitment to data security. Remember, a proactive approach to incident response is essential to protecting your organization’s reputation and operations.
















Add Comment