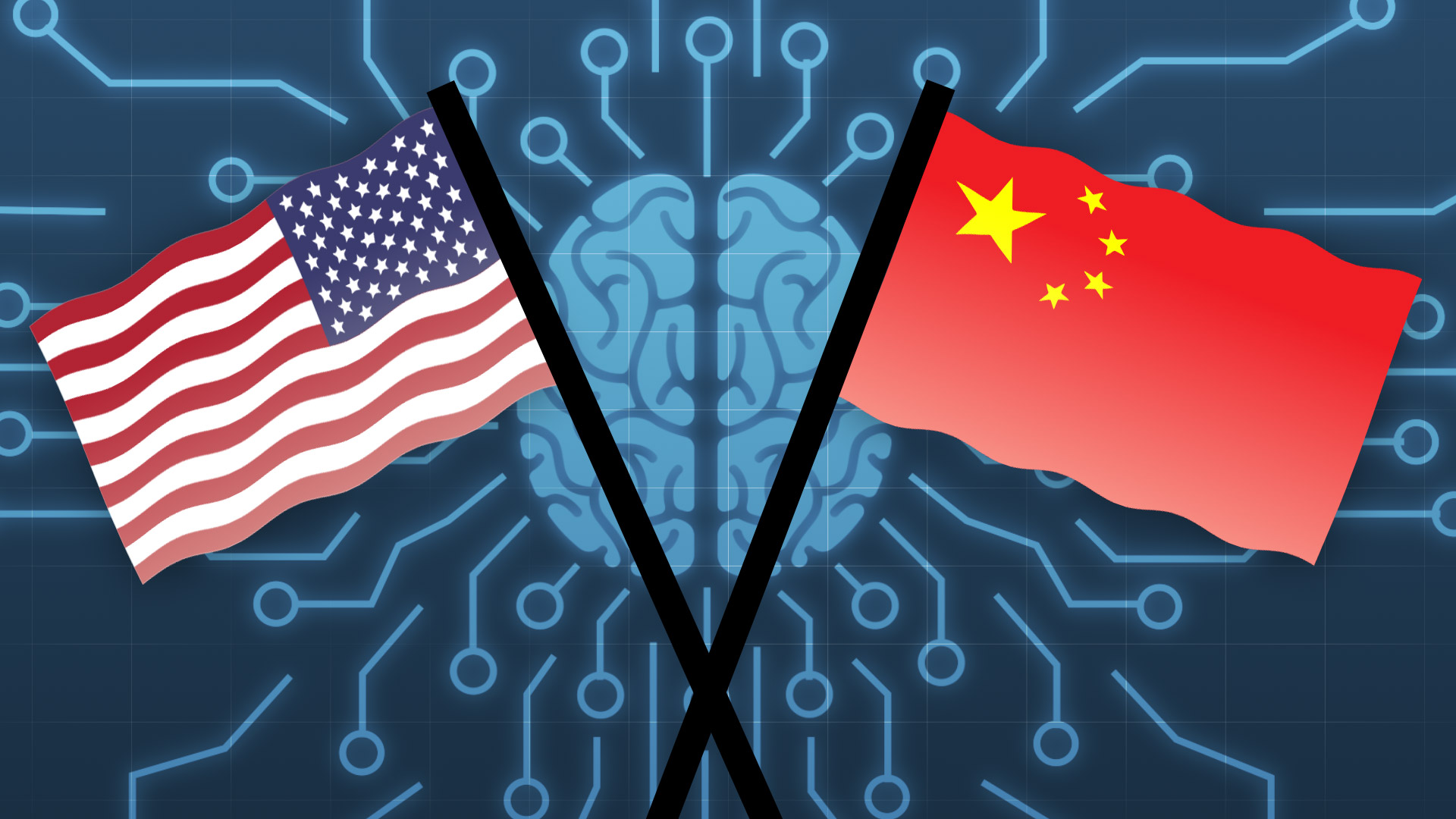
A fierce global technology race is underway, with leading nations pouring massive investments into the development of ultra-powerful AI supercomputers. Dubbed the “Silicon Sprint”, this race goes far beyond mere economic or technological competition.
The quest for superior AI computing power ties directly into geopolitical dominance in the 21st century digital era. It holds monumental implications for economic competitiveness, national security, global influence and even ethical risks.
As nations sprint to build the next generation of super-intelligent AI machines, the world is witnessing a high-stakes showdown between technology superpowers.
Why Nations Are Racing for AI Supremacy
What factors are driving this breakneck race to develop artificial intelligence supercomputers with unprecedented processing brawn?
The Economic Imperative
Cutting-edge AI systems require massive computational muscle to ingest, process and gain insights from huge datasets. Leading the silicon sprint provides countries a decisive innovative edge across areas like:
- Pharmaceutical research
- Materials science
- Climate modeling
- Energy grid optimization
- Supply chain analytics
- Predictive modeling
Nations commanding superior supercomputing capabilities are best positioned to power AI breakthroughs across these sectors, conferring major economic advantages.
The Security Factor
AI supercomputers also enable unmatched intelligence, defense and military capabilities including:
- Analyzing satellite data for threats
- Simulating complex battlefield scenarios
- Cryptography and code breaking
- Predicting and thwarting cyberattacks
- Tracking disinformation campaigns
In an era where information superiority means security superiority, leading the silicon sprint serves as a geopolitical insurance policy.
Global Tech Supremacy
Beyond economic and defense gains, the sprint also revolves around global tech leadership and prestige. Building the world’s most advanced supercomputer signals a nation’s unrivaled innovation capabilities.
It cements supreme credibility, soft power and influence in steering emerging technology standards across the globe.
The Major Players in the AI Supercomputing Arena
The silicon sprint has set the stage for a high-stakes showdown between three superpowers:
United States
With historical dominance in computing tech, the US remains a leader in supercomputers. American systems currently hold the top two positions globally, including:
- Frontier – Ranked #1, capable of over 1.5 exaflops of processing power
- Summit – Previously #1, capable of over 200 petaflops
The US employs an open-source model focused on academic-industry partnerships, with companies like IBM, Nvidia, and Hewlett Packard powering development.
China
China has emerged as a top contender, producing homegrown systems like:
- Sunway TaihuLight – #3 globally, over 125 petaflops
- Tianhe series – Multiple top 10 machines including Tianhe-1A and Tianhe-2
Unlike the US, China funnels heavy state funding into central research hubs like the National Supercomputing Centers to drive self-reliant innovation.
European Union
While behind the US and China, the European Union remains firmly in the race by co-funding initiatives like:
- The LUMI supercomputer – #2 globally, over 150 petaflops
- The Leonardo supercomputer – Over 240 petaflops planned
The EU pools funding and research across member states to develop world-class high performance computing capabilities.
The Race Beyond Processing Power Alone
While benchmarks like petaflops and exaflops signal raw computing brawn, the sprint extends far beyond sheer processing speed.
The race to build intelligent supercomputers also involves major strides around supporting areas like:
Quantum Computing
Quantum computing harnesses unique quantum mechanical phenomena to carry out specialized processing beyond classical systems. By leveraging quantum principles like superposition and entanglement, nations aim to unlock unprecedented capabilities for areas ranging from material science to drug discovery.
Neuromorphic Chips
Neuromorphic computing seeks to emulate the workings of the human brain using highly efficient chip architectures. Pioneers like Japan are leading research around brain-inspired systems to excel at processing optimization problems in real-time.
Software and Algorithms
Sophisticated software and optimization algorithms are crucial to extract maximal value from the hardware. Key investments are flowing into areas like:
- Parallel programming frameworks
- Data analysis and visualization
- AI model tuning
- Accelerated computing libraries
Leadership across these infrastructure pillars ensures nations draw full returns on their massive supercomputer investments.
Where This Race Could Lead: Geostrategic Implications
The silicon sprint seems poised to confer sizeable advantages to frontrunners. But it also risks digitally Balkanizing the world across several fronts.
Economic Divides
Quantum leaps in computing confer competitive edges in commercial innovation, leaving laggards behind. Nations lacking cutting edge supercomputers face growing disadvantages in sectors like biotech, finance, telecoms and more as rivals reap efficiency gains.
This widens both regional and cross-country economic inequalities, as rewards mainly accrue to leaders who develop or access ultra-advanced AI systems.
New Power Dynamics
Computationally dominant states expand their influence in setting digital governance priorities around data flows, technical standards and AI accountability models.
This rebalances international policymaking power, potentially diluting the heft of historically influential blocs falling behind in the sprint.
Destabilizing Technologies
Unchecked development of technologies like autonomous weapons or mass surveillance tools powered by rogue AI supercomputers poses complex legal and ethical dilemmas.
Without reasonable safeguards governing responsible design and use, such capabilities risk severely undermining global security.
An Arms Race With Ethical Stakes
While the silicon sprint promises enormous economic potential, it remains fraught with ethical landmines if handled recklessly.
Entrenching the Digital Divide
Concentration of extreme-scale computing power risks marginalizing vulnerable communities without the resources to access such tech.
Algorithmic Bias at Scale
Supercomputers like AI systems risk severely amplifying biases that enter training pipelines. At their massive scale, the resulting discrimination could deprive millions of opportunities.
A Surveillance State?
The unchecked spread of mass surveillance powered by rogue AI supercomputers and lax data protection poses risks to civil liberties across societies.
Towards Responsible Leadership
Harnessing AI’s upsides while containing its risks calls for responsible development anchored in ethics of shared benefit.
The ideal approach should:
- Spread tech gains equitably beyond narrow national interests to uplift vulnerable groups.
- Ingrain standards for algorithmic transparency and oversight early before harmful practices become entrenched.
- Encourage international collaboration and open publication of research gains.
The silicon sprint is accelerating rapidly, amplifying risks. Its destabilizing fallouts calls for enlightened leadership balancing ambitious innovation with ethical responsibility.













Add Comment